BYOD Security for Employees: Protecting Both Your Work and Personal Data

You love the convenience of using your personal device for work. We all do—96% of employees have reported using a personal device for work.
Personal devices are familiar, always with you, and save you from juggling multiple gadgets.
The vast majority of employers are also fans of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) programs. 4-out-of-5 organizations encourage employees to use their own devices—probably because they see a 68% jump in productivity with BYOD, and save money in the process.
While using your own devices offers great flexibility, it also comes with its own set of risks.
We’ve written extensively about BYOD policies and BYOD security best practices from an employer’s perspective. But this article is specifically for employees—what are the steps you should take to protect both yourself and your company.
8 Steps to Protect Yourself and Your Organization
1. Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Why It Matters: Strong passwords and MFA add layers of security, making it harder for unauthorized users to access your device and the data it contains.
Some studies estimate that more than 40% of data breach events are caused by lost or stolen devices—with some industries like healthcare experiencing an even higher percentage of data breaches due to loss or theft.
2. Keep Your Software Up to Date
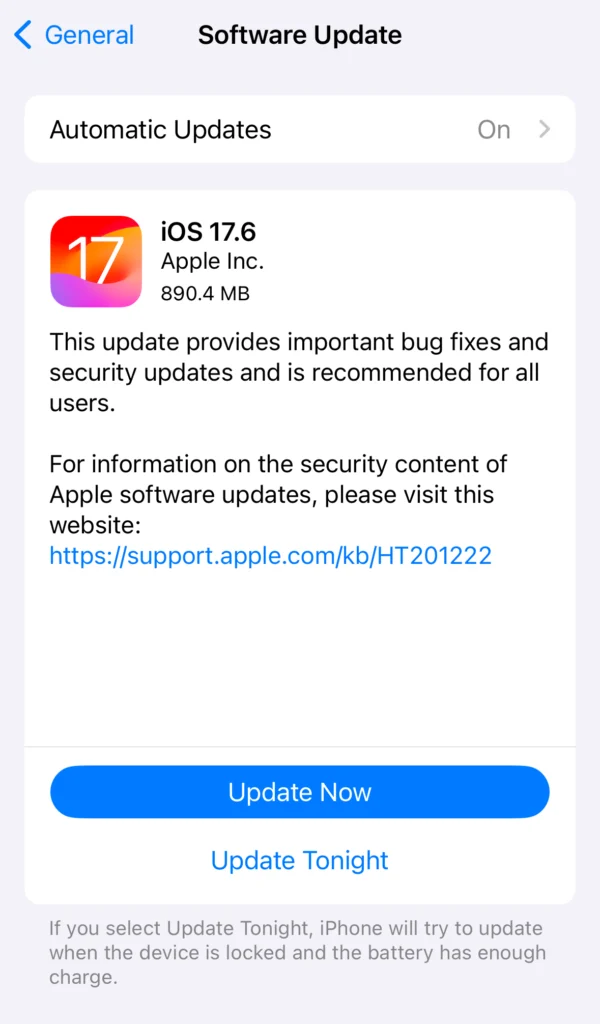 Why It Matters: Regular updates fix vulnerabilities and protect against the latest threats. Cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to exploit software weaknesses. Outdated software can leave your device vulnerable to malware, ransomware, and other cyberattacks.
Why It Matters: Regular updates fix vulnerabilities and protect against the latest threats. Cybercriminals are constantly finding new ways to exploit software weaknesses. Outdated software can leave your device vulnerable to malware, ransomware, and other cyberattacks.
Keeping your software up to date gives you the latest security patches and enhancements, providing a stronger defense against potential breaches. Regular updates also improve the performance and functionality of your device so that it runs smoothly and efficiently.
- iPhone: Go to Settings > General > Software Update.
- Android: Go to Settings > System > Advanced > System update.
- Mac computer: Use System Preferences > Software Update.
- Windows computer: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.

3. Avoid Public Wi-Fi Networks If You Can—Use a VPN If You Can’t or Use Your Cellular Provider's Network.
Why It Matters: Public Wi-Fi networks are notoriously unsecured, making it easy for hackers to intercept your data. When you connect to an open network, you expose your device to various threats, such as man-in-the-middle attacks, where hackers can eavesdrop on your communications and steal sensitive information like login credentials, financial details, and personal messages.
Public Wi-Fi hotspots are often prime targets for cybercriminals looking to deploy malware or phishing schemes. Using a VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it much harder for anyone to access your data, and better safeguarding your personal and work-related information while using these networks. Data being sent via 4G is also encrypted, making 4G safer than public Wi-Fi.
4. Separate Work and Personal Data
Why It Matters: This should be fairly obvious, but mixing personal and work data can lead to accidental data breaches and privacy issues.
Unintended emails sent from personal accounts, or saving a work PDF to your own Google Drive are just two examples.
On the flip side, you don’t want your personal information accessed by your organization. Financial, medical, and personal information and messages should stay private.
- iPhone: Use apps like Microsoft Outlook for work emails and keep personal emails separate.
- Android: Use work profiles through Settings > Accounts > Add work account.
- Mac computer: Use separate user accounts via System Preferences > Users & Groups.
- Windows computer: Create separate user profiles through Settings > Accounts > Family & other users.
5. Apply the Same Security Vigilance on Your Personal Device as You Do With Your Work Devices

Why It Matters: Many of us drop our security awareness when moving from a work device to a personal device. This lapse can expose both personal and work-related information to risks. Compounding the risk is the fact that for most of us, the security on our personal accounts and devices is not as robust as our accounts and devices at work.
Phishing attacks often come in the form of deceptive emails, messages, or websites that appear legitimate but are designed to steal your credentials. Users on mobile devices are three times more likely to fall for phishing attacks compared to desktops, so think twice thrice when using your personal phone to check a work email.
6. Report Security Incidents Immediately
Why It Matters: Prompt reporting can help mitigate damage and prevent further incidents. When it comes to our personal devices, many of us hesitate to report security incidents due to concerns about privacy, fear of repercussions, or simply the belief that it’s not serious enough. However, failing to report these incidents can have far-reaching consequences, not only for your personal data but also for your organization’s security.
Personal devices often contain a mix of work-related and personal information. A breach on your personal device can provide attackers with a gateway to your company's network, leading to more severe and widespread damage. Early reporting allows IT teams to act swiftly, containing the threat and minimizing its impact.
Common incidents that should be reported include:
- Phishing Attempts: Even if you did not fall for the scam, reporting the attempt can help protect others.
- Malware Infections: Strange pop-ups, slow performance, or unrecognized applications may indicate malware.
- Lost or Stolen Devices: Immediately report any loss or theft to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Suspicious Activity: Any unexpected changes or unfamiliar activity on your device should be flagged.
Remember, the goal of reporting is not to place blame but to enhance security for everyone. By overcoming hesitation and promptly reporting incidents, you contribute to a safer and more secure digital environment for both your personal and professional life.
7. Regularly Review and Manage Permissions
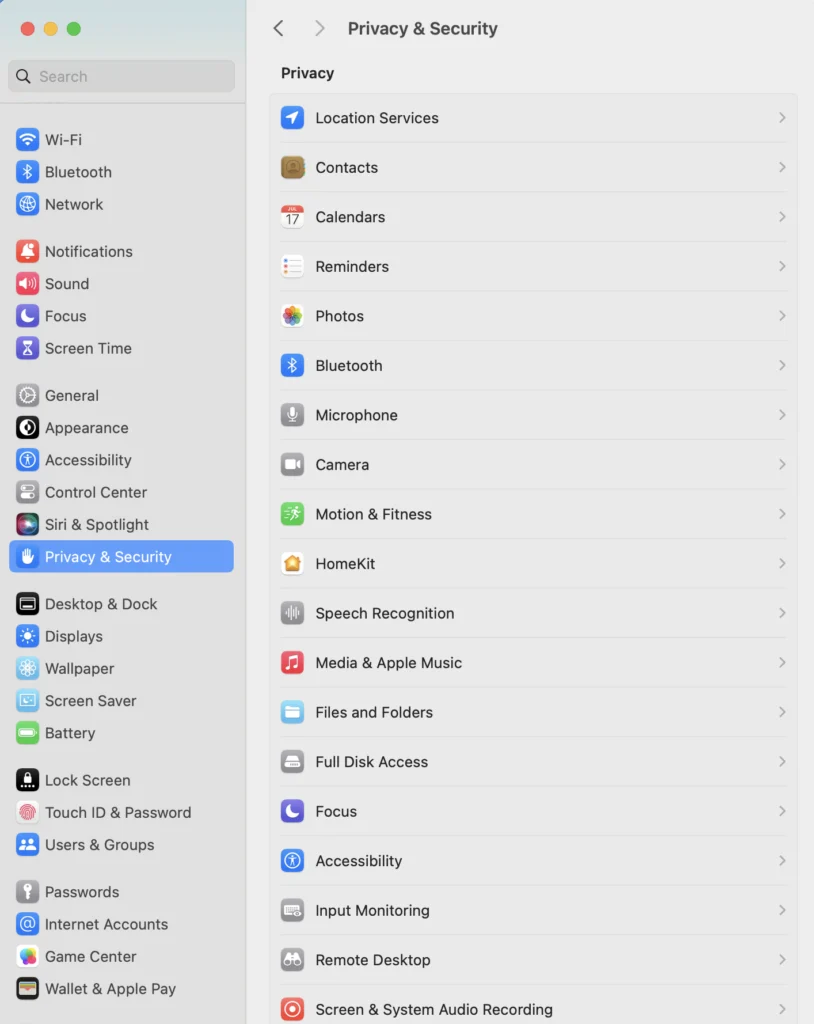 Why It Matters: Some employer-mandated apps and services may request extensive permissions that could infringe on personal privacy. When you install apps for work, they might request access to various parts of your device, such as your contacts, camera, location, or even your personal data. While these permissions are often necessary for the apps to function correctly, they can also pose significant privacy risks if not managed properly.
Why It Matters: Some employer-mandated apps and services may request extensive permissions that could infringe on personal privacy. When you install apps for work, they might request access to various parts of your device, such as your contacts, camera, location, or even your personal data. While these permissions are often necessary for the apps to function correctly, they can also pose significant privacy risks if not managed properly.
Unchecked permissions can lead to unintended data sharing, allowing apps to access more information than necessary. This often blurs the lines between your personal and professional life, exposing your private information to your employer or third-party service providers.
- iPhone: Review app permissions in Settings > Privacy & Security
- Android phone: Review permissions through Settings > Apps & notifications > App permissions.
- Mac laptop: Go to System Preferences > Privacy & Security to manage permissions.
- PC laptop: Manage app permissions through Settings > Privacy > App permissions.
8. Backup Your Personal Data Regularly
Why It Matters: If your employer needs to wipe your device remotely—and has the required permissions to do so—due to a security incident, you could lose personal data. In the unfortunate event of a security breach, companies might resort to remotely wiping devices to protect sensitive information. While this action could be crucial for safeguarding corporate data, it can inadvertently lead to the loss of your personal files, photos, and other important information stored on the same device.
Regularly backing up your personal data allows you to have a secure copy of your important information, independent of your device's status. This will protect against data loss not only from remote wipes but also from device theft, malfunction, or accidental damage. By maintaining up-to-date backups, you can quickly restore your personal data, minimizing disruption to your personal life and avoiding the permanent loss of valuable information.
Safe BYOD for All
Bringing your own device to/for work offers great flexibility and convenience, but it also brings significant responsibilities and risks. As you’ve read, there are actionable steps you can take to protect both your personal data and your organization’s sensitive information.
By implementing BYOD best practices like strong passwords and MFA, keeping your software up to date, using VPNs on public Wi-Fi, separating work and personal data, applying consistent security vigilance, reporting incidents promptly, managing permissions regularly, and backing up your data, you can practice safe BYOD.
Your security practices not only protect you but also your company from potential breaches. It's about maintaining a balance—enjoying the convenience of BYOD while being mindful of the security implications.
Stay vigilant, stay informed, and prioritize security in every aspect of your digital life.